Rising Cybersecurity Threat Calls for Strategic Realignment in the Public Sector
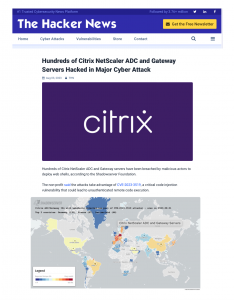
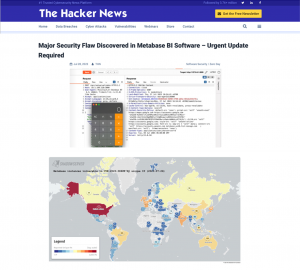
Africa’s Cybercrime landscape is a cause for great concern. In Interpol’s latest African Cyberthreat Assessment Report it clearly indicates the rising threat of cybercrime for governments. The rapid advancement and interconnectivity of technology is a breeding ground for complex attacks and criminals are exploiting new methods of infiltration in order to access confidential data and sensitive information. Ransomware attacks on public sector entities have crippled major operations and systems incurring exorbitant losses. According to Interpol’s report, the impact of malicious programs should not be underestimated.
The proliferation of ransomware has resulted in a rise in financially motivated cybercrime activities across Africa. This increasingly severe threat will be addressed at the upcoming Public Sector Cybersecurity Summit on 3 October 2023 (#PubliSec2023) in Johannesburg South Africa.
Shadowserver also reported that South Africa is the nation most targeted by ransomware attacks, accounting for 42% of all detected attacks. Morocco is next with 8%, Botswana and Egypt at 6%, Tanzania and Kenya each account for 4% of detected ransomware attacks.