Over 1,200 Citrix servers unpatched against critical auth bypass flaw
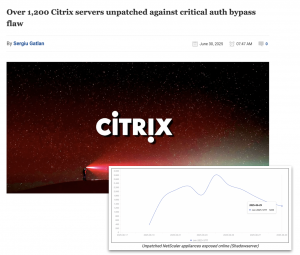
Over 1,200 Citrix NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway appliances exposed online are unpatched against a critical vulnerability believed to be actively exploited, allowing threat actors to bypass authentication by hijacking user sessions.On Monday, security analysts from the internet security nonprofit Shadowserver Foundation have discovered over the weekend that 2,100 appliances were still vulnerable to CVE-2025-5777 attacks. Shadowserver also found over 2,100 NetScaler appliances unpatched against another critical vulnerability (CVE-2025-6543), now actively exploited in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.